Most of you are curious in what the so-called next era of the internet will look like when web3 comes into being. Is it only trendy jargon or a revolutionary concept? How will web3 impact your online presence and the way you connect with audiences—from building a website to branding and marketing your talents—especially for independent creatives and small enterprises.
What is Web 3: How does the future of internet seem to be.
Although there is still much to learn about web3, discussions about its ambitions, technology, potential advantages, and potential drawbacks are already taking place among specialists, proponents, and detractors. And numerous businesses and sectors have started incorporating certain key web3 elements.
In this essay, I'll go over all you need to know about the current state of our internet's evolution, including what web3 is, its distinguishing features, and how it might affect our online communities.
What is web3?
The web3 we're talking about refers to the internet infrastructure that is now being built, but it hasn't fully arrived yet. The future internet, according to supporters of web3, aims to offer a more specialized, intelligent, and autonomous browsing experience than the one we have right now.
The phrase "web3" was first used in 2014 by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood. It is based on a theory known as "web 3.0" or "The Semantic Web," which was popularized by Tim Berners-Lee. In an interview with Wired in 2021, Wood summarizes his web3 vision: "More truth, less trust."
There is a lot of interest in Web3 because it promises to use blockchain technology to build a decentralized internet ecosystem. According to the New York Times, venture capital firms invested more than $27 billion in cryptocurrency-related projects in 2021, with a large portion going toward developing web3. But even brands that cater to consumers have joined the web3 craze. Reddit is reportedly tokenizing "Karma Points" on its platform in order to get ready for cryptocurrency technology. Nike recently acquired the digital fashion company RTFKT, joining the many other fashion companies preparing for a digital transformation.
A few pessimists counteract each optimist's overconfidence. Nobody can comment on web3's successes or failings because it hasn't been completely implemented. Web3 is now more tangible than just an abstract idea thanks to a few well-known applications. Additionally, our post-pandemic global mindset is battered but welcoming to what comes next.
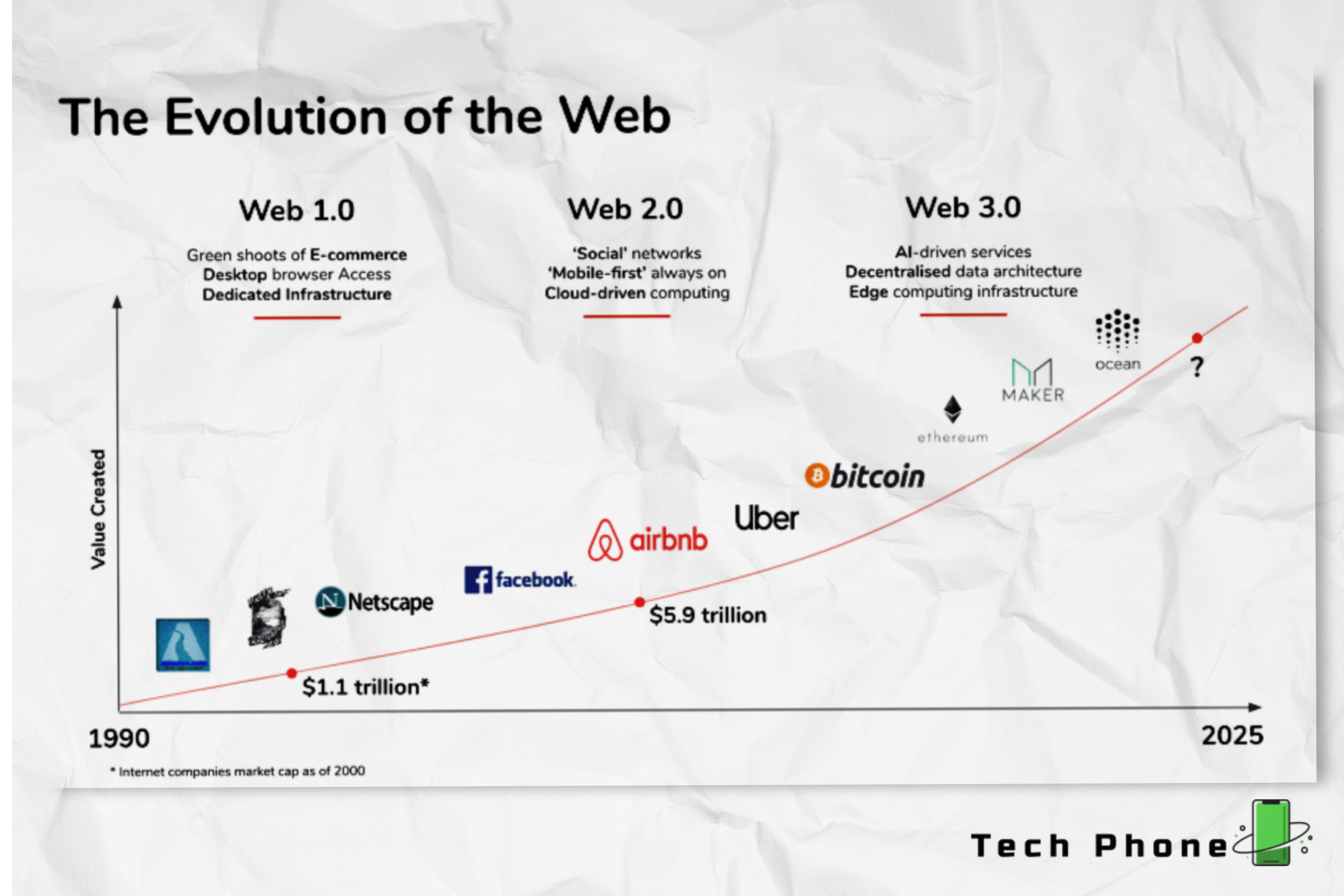
The evolution of the internet: what has the web been like so far?
Have we entered a new phase in the development of the internet? Let's start by examining what makes Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 distinct from one another. We can better comprehend how the internet evolved by placing our current usage in its historical context.
 |
| The evaluation of the web |
Web1 (1991-2004):
The internet of Web 1.0 is the internet of the 1990s. Consider a previous iteration of the internet that had message boards and websites like AOL and Netscape for those who didn't experience it or need a refresher. Users benefited from a primarily read-only internet at this time because web design was still in its infancy.
Users rarely interacted with web1's static web page-based interface. In addition, the majority of websites belonged to large corporations, and there was hardly any user-generated material, which is possibly one of the biggest differences between web1 and web2.
 |
| AOL's interface from 2000 is a great representation of the late web1 era |
Web2 (2004 - present day):
The internet you now use is Web 2.0. Web2 operates as an online user-centered ecosystem and is also referred to as the "social web." Early on in the development of the web2, websites like Facebook (later renamed Meta), Google, YouTube, and eventually eCommerce systems like Amazon were to be established with the help of technologies like Javascript, HTML5, and CSS3. Due to this, the web 2 has become platform-driven and is reliant on user-generated content, social media, engagement, and interactive design to succeed (with an increasing emphasis on UX design principles).
Web2 is the centralized internet era, in which Big Tech (organizations like Google and Meta, for instance) owns and controls data distribution. In addition to receiving information through browsing, businesses also provide information to us, which we frequently trade for services. For targeted advertising, they employ this information.
During web2, increased mobile usage contributes to the internet's exponential growth. The invention of apps altered how people connect, consume, and create content, goods, and services by encapsulating everything we require in an easily accessible user interface.
 |
| The evolution of Facebook's interfaces from 2005 to 2009 ,and 2010 |
Defining the components and features of web3
We are unable to go into detail about how to create a website or get your company ready for this new era because it is too early to define web3 precisely. To better comprehend the future vision for web3 and how it will differ from the web we know today, we can still take a closer look at the emerging principles and enabling technologies.
Semantic Web is the foundation of Web3, which Berners-Lee designed as a "web of data" and a collaborative platform where we might all come together to read and publish.
Top development technologies driving the web3:
- Blockchain technology: The decentralization of the present web will be fueled by blockchain, which is web3's digital database. Users may now safely produce, store, and manage data thanks to technology without the need for a middleman.
- Decentralization: Data, applications, and services will be dispersed without a central authority and stored in several places on the blockchain, allowing users more control and reducing the opportunity for Big Tech firms like Meta and Google to use information for targeted advertising.
- Advanced machine learning will enable more intelligent interactions between apps and user interfaces thanks to artificial intelligence.
- A decentralized, safe currency built on blockchain ledgers is known as cryptocurrency (for example, Ether or Bitcoin.) The currencies, banks, and payment processors we currently use on web2 will be substantially replaced by cryptocurrency.
- DeFi (decentralized finance): Using a similar blockchain technology to cryptocurrencies, DeFi (decentralized finance) would eliminate middlemen from internet transactions.
- Online services will be managed by DAOs (decentralized autonomous organizations), or user-owned communities without centralized authority. Examples include cryptoco-ops and investor organizations that buy NFTs collections, fund businesses, and more using cryptocurrencies like Etheruem.
- Decentralized applications, or dApps, are web3's term for web applications that operate on peer-to-peer blockchain networks. Participants in dApps can simultaneously feed and consume content without outside interference, in contrast to current web apps where one entity (often the company) controls the backend.
- User autonomy: A decentralized web3 promotes total user autonomy by enabling a permissionless, democratized, censorship-free web where anybody can participate and own a piece of the web.
- User privacy: Web3's AI technologies will let users keep their true identities separate from their online personas. Web3 wants to make it more difficult for businesses to access people's personal information and browsing history thanks to blockchain technology's heightened data security.
Web3 as we know it today
The web3 category includes many currently in use technologies. Some of the technologies listed above are likely familiar to you, and you may have even utilized them. Despite the fact that none of these developments fully embody the web3 environment, they are gradually shaping it:
Brands in the Metaverse
The interactive, immersive, and all-encompassing social media platform promises to open up a brand-new virtual universe for the creative economy. Even if the term "metaverse" is ambiguous, many businesses are experimenting with VR and AI technology to protect their brand in the future. Top examples include the introduction of digital fashion collections for avatars by Balenciaga, Prada, and Thom Browne, as well as the organization of NFT shows in the Metaverse by the Institute.
The NFT hype
A blockchain stores an NFT, which is a special digital data unit. With the ability to prove digital file ownership, they have already changed the gaming, collectibles, and art industries. On digital marketplaces powered by cryptocurrencies today, numerous artists produce and market NFTs.
Investment in cryptocurrencies
The widespread acceptance of cryptocurrencies is difficult to deny. Since the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, a large number of people and businesses have been motivated by the philosophy of the new economic system and invested in more than 4,000 other varieties of cryptocurrencies.
Limits and early criticism of web3
But web3 is not just marketing speak. Even with cutting-edge decentralizing technology, some of the web's early detractors are dubious about its viability.
Others argue that blockchain technology is simply too new to be used and evaluated at this point. Although the IT industry has previously gone through the appealing concepts behind web3, Tim O'Reilly, author of What is Web 2, observes that the system is still too undeveloped to bridge the gaps between decentralized technologies and non-web3 assets and services.
O'Reilly wrote in Why It's Too Early to Enthusiasm for Web 3:
If web3 is to become a general-purpose financial system or a broad system for decentralized trust, it must build strong interfaces with the real world, its legal systems, and the functioning economy.
The tech community is on edge thanks to Molly White, another web3 skeptic. The software developer is in charge of the blog Web3 Is Going Just Great, a freely accessible tool that details web3's murky underbelly. As information about fraud and corruption in the NFT and cryptocurrency markets becomes available, White updates her website in real-time. She also makes comments of the effects that early web3 players had on the environment, society, and economy.
The viability of web3 is also contested by several critics. Despite the fact that the openness of blockchain technologies encourages businesses and organizations to support and raise funds for environmental causes, the environmental costs of these transactions are high. To highlight these issues and lessen web3's environmental impact, certain groups already work.


Comments
Post a Comment